Integrate Microfrontends into OneCX
The script toggle-mfes.sh integrates a locally running microfrontend into the OneCX environment, allowing it to interact with other microfrontends. This process is also reversible.
- How it works
-
The script creates a small configuration file in Traefik, tailored to the local microfrontend. Traefik then forwards requests from the Docker network to the external local microfrontend. The script can be run from the root directory of the onecx-local-env repository.
The Traefik configuration files are stored in
init-data/traefik/active/. Traefik immediately detects any changes there, no extra restart is necessary.
./toggle-mfes.sh -l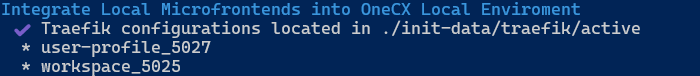

Precondition
Before a microfrontend can be successfully integrated into OneCX, it must be started. It is recommended to start the microfrontend in the following way. In the following examples, 6021 is used as the port where the microfrontend is running locally. Adjust the port as needed.
npm run start -- --port 6021 --host 0.0.0.0 --disable-host-check --public-host=http://localhost:6021npm run start -- --port=6021 --host 0.0.0.0 --disableHostCheck --publicHost=http://localhost:6021|
Please check the microfrontend is up and running by accessing the public host URL in Browser. The remoteEntry.js should be loaded - the content is displayed. |
Available Options
The script accepts multiple options to customize its behavior; one of each is required.
All options may only be used separately!
The options are:
- -a <app-name>[:<app-port>[:<app-path>]]
-
Integrate one or more local microfrontends (app-name). In addition to the microfrontend name, you can optionally specify a port (app-port) and path (app-path). The default port is 4200. See example section below.
If the microfrontend is one of OneCX Core products and no port is specified then predefined ports are used. - -c
-
Cleanup, remove all existing configurations
- -d <app-name>[:<app-port>]
-
Deintegrate one or more local Microfrontends. See example section below.
-
During deintegration, the same port must be specified as was specified during integration.
-
Deintegrate your microfrontend before stopping it, otherwise Traefik will continue to route requests to a non-existing service. There is no failover mechanism. See section below for details.
-
- -h
-
Display this help and exit
- -l
-
List of currently integrated local microfrontends
Examples
Integrate my App with specific path
The local microfrontend my-app runs on http://localhost:4200 (standard Angular).
/my-app-path is the path under which the microfrontend is accessible within OneCX.
./toggle-mfes.sh -a my-app::/my-app-path
Integrate several Apps
Integrate workspace on standard port 5025 AND user-profile on port 5027.
Since no path is specified, the default paths are used, e.g. /mfe/workspace
./toggle-mfes.sh -a workspace user-profile:5027
Integrate OneCX Shell
The integration of the shell requires a special path mapping. Hereby the path is not completely stripped. Define the strip path to be used at the end.
./toggle-mfes.sh -a shell::/onecx-shell/:/
| Because OneCX Shell is a microfrontend with a special role in OneCX it have to be started with a specific command as well. |
npm run start:local-envnpm run start:local-env -- --port=5000 --public-host=http://localhost:5000Deintegrate my App
The -d option allows you to undo an integration. The same rule applies to the port: if the port is not 4200, it must be specified.
./toggle-mfes.sh -d my-app:12345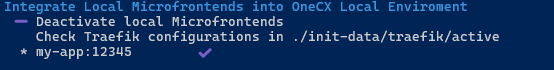
Deintegrate ALL Apps
The Traefik configurations are being cleaned up: All specific configuration files for the Microfrontend integration are being deleted.
./toggle-mfes.sh -c
|
Microfrontends integrated using the methods described above take priority over those run via Docker Compose. If the microfrontends started with Docker Compose are needed again, the locally integrated microfrontends must first be deintegrated using the -d option. A failover mechanism is not implemented due to differing path reductions. |
Routing & Priorities
As described earlier, Traefik is responsible for routing. Each route is assigned a priority, which Traefik derives by default from the length of the rule: the longer the rule, the higher the priority. To avoid routing collisions, the local microfrontends are configured with a significantly higher priority.
This means you can run multiple microfrontends with the same routing rule in parallel and still control which microfrontend is used in OneCX. This is very useful if you want to use locally running microfrontends without having to stop the corresponding service in Docker Compose.
The Traefik configuration generated when integrating a microfrontend (see above) sets a significantly higher priority for this route, so that the local microfrontend is used preferentially.
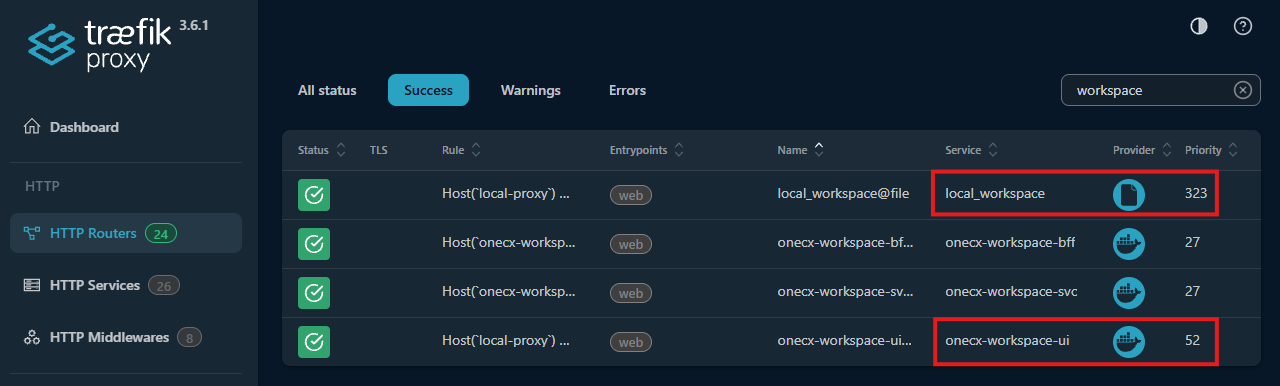
Example: Prioritize local Microfrontend
In this example, the OneCX Workspace microfrontend is running both in Docker Compose (Service: onecx-workspace-ui) and locally (Service: local_workspace). The local instance is used preferentially because it has a higher priority (323) than the Docker Compose instance (52).