Networking in OneCX Local Environment
This document explains how networking is configured and managed in the OneCX Local Environment.
Docker Resource Names
To isolate the local OneCX environment from the host system and other Docker environments, Docker uses the project name onecx-local-env. This project name serves as a prefix for all created Docker resources (containers, networks, volumes), ensuring seamless communication between all services while minimizing disruptions and conflicts.
The following Docker resource names and prefixes are used in the OneCX Local Environment:
| Project Name |
|
| Network Name |
|
| Container Prefix |
|
Network Actors and Components
The OneCX Local Environment uses a sophisticated networking setup that combines:
-
Traefik
-
Service Discovery and Routing
-
Docker Compose Network
-
Host file Configuration
-
Environment Configuration
Traefik
Traefik serves as the central entry point for all HTTP traffic in the OneCX environment. It acts as:
| Reverse Proxy |
Routes incoming requests to appropriate backend services |
| Load Balancer |
Distributes traffic across service instances |
| Service Discovery |
Automatically detects new services through Docker labels |
| API Gateway |
Provides a single entry point for all microservices |
| Configuration |
The Traefik configuration is split across multiple files:
|
| Traefik Settings |
|
entryPoints:
web:
address: ":80" # HTTP entry point
providers:
docker:
endpoint: unix:///var/run/docker.sock
file:
directory: /etc/traefik/active
watch: truePls. aware the locations of Traefik configuration files are mapped as follows:
init-data/traefik/base/traefik-conf.yml => /etc/traefik/traefik.yml init-data/traefik/active => /etc/traefik/active
Service Discovery
- Traefik Labels
-
Services register themselves with Traefik using Docker labels:
labels:
- "traefik.http.services.<service-name>.loadbalancer.server.port=8080"
- "traefik.http.routers.<service-name>.rule=Host(`<service-name>`)"labels:
- "traefik.http.services.<ui-service-name>.loadbalancer.server.port=8080"
- "traefik.http.routers.<ui-service-name>.rule=Host(`onecx.localhost`) && PathPrefix(`/<app-path>/`)"Service Routing Rules
Different routing patterns are used for different service types:
Host(`service-name`)Host(`onecx.localhost`) && PathPrefix(`/app-path/`)Port Mapping Strategy
- External Ports (Host → Container)
-
Key external ports exposed to the host:
Service Host Port Purpose Traefik HTTP
80
Main HTTP entry point
Traefik Dashboard
8082
Web UI for Traefik management
Keycloak
8080
Identity and access management
PostgreSQL
5432
Database direct access
- Internal Ports (Container → Container)
-
Services communicate internally using standard ports:
| Web Services |
Port 8080 (Quarkus default) |
| PostgreSQL |
Port 5432 |
| Frontend Applications |
Port 8080 (Nginx) |
Docker Compose Network
Here only the v2 edition is described. The v1 edition is similar but uses the example network.
Central configuration of the Docker Compose network is defined in versions/v2/compose.yaml
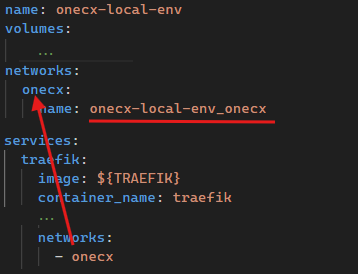
The network alias used by the services is onecx. On project level the network is named onecx-local-env_onecx. This is also the name visible when executing docker network ls. See section at the top of this document about the Docker resource names.
- Network Features
| Service-to-Service Communication |
Services can communicate using container names as hostnames |
| Automatic DNS Resolution |
Docker provides built-in DNS for container name resolution |
| Network Isolation |
Traffic is isolated from the host network and other Docker networks |
| Network Communication Patterns |
Services communicate using these patterns |
| Communication Type | Example | URL Pattern |
|---|---|---|
Frontend to BFF |
Shell UI → Shell BFF |
|
BFF to Service |
Shell BFF → Theme Service |
|
Service to Database |
Theme Service → PostgreSQL |
|
Service to Keycloak |
Any Service → Keycloak |
Host File Configuration
Check the hosts entries section for detailed instructions.
Environment Configuration
Within the Docker Compose files (compose.yaml), several environment variables are used to manage settings for services:
The source of the environment variables is located in the version folder: versions/v2/.env.
Here the Link to GitHub source file.
Environment variables used in Docker Compose
versions/v2/.env########################################
############## GENERAL #################
########################################
COMPOSE_PROJECT_NAME=onecx-local-env
COMPOSE_CONVERT_WINDOWS_PATHS=1
JSON_LOGGER_ENABLED=false
########################################
############# BASE Services ############
########################################
TRAEFIK=traefik:3.6.1
POSTGRES=docker.io/library/postgres:15.5
PGADMIN=dpage/pgadmin4:latest
KEYCLOAK=quay.io/keycloak/keycloak:26.2.0
########################################
########## OneCX Variables #############
########################################
KC_REALM=onecx
KC_APP_NAME=keycloak-app
KC_URL=http://${KC_APP_NAME}
KC_CLIENT_ID=onecx-shell-ui-client # Client ID set in shell environment
...Environment variable sets defined in Docker Compose
versions/v2/compose.yaml...
x-bff-variables: &bff_environment
ONECX_PERMISSIONS_ENABLED: ${ONECX_PERMISSIONS_ENABLED}
ONECX_PERMISSIONS_CACHE_ENABLED: ${ONECX_PERMISSIONS_CACHE_ENABLED}
QUARKUS_OIDC_CLIENT_CLIENT_ID: ${ONECX_OIDC_CLIENT_CLIENT_ID}
QUARKUS_OIDC_CLIENT_CREDENTIALS_SECRET: ${ONECX_OIDC_CLIENT_S_E_C_R_E_T}
QUARKUS_OIDC_CLIENT_AUTH_SERVER_URL: ${ONECX_AUTH_SERVER_URL}
QUARKUS_OIDC_AUTH_SERVER_URL: ${ONECX_AUTH_SERVER_URL}
TKIT_LOG_JSON_ENABLED: ${JSON_LOGGER_ENABLED}
TKIT_SECURITY_AUTH_ENABLED: ${ONECX_SECURITY_AUTH_ENABLED}
x-svc-variables: &svc_single_tenancy
QUARKUS_LOG_LEVEL: ${ONECX_LOG_LEVEL}
QUARKUS_OIDC_AUTH_SERVER_URL: ${ONECX_AUTH_SERVER_URL}
QUARKUS_OIDC_CLIENT_CLIENT_ID: ${ONECX_OIDC_CLIENT_CLIENT_ID}
QUARKUS_OIDC_CLIENT_CREDENTIALS_SECRET: ${ONECX_OIDC_CLIENT_S_E_C_R_E_T}
QUARKUS_OIDC_CLIENT_AUTH_SERVER_URL: ${ONECX_AUTH_SERVER_URL}
QUARKUS_DATASOURCE_JDBC_MIN_SIZE: ${ONECX_DATASOURCE_JDBC_MIN_SIZE}
QUARKUS_DATASOURCE_JDBC_MAX_SIZE: ${ONECX_DATASOURCE_JDBC_MAX_SIZE}
QUARKUS_DATASOURCE_JDBC_IDLE_REMOVAL_INTERVAL: ${ONECX_DATASOURCE_JDBC_IDLE_REMOVAL_INTERVAL}
TKIT_LOG_JSON_ENABLED: ${JSON_LOGGER_ENABLED}
TKIT_SECURITY_AUTH_ENABLED: ${ONECX_SECURITY_AUTH_ENABLED}
x-svc-multi_tenancy: &svc_multi_tenancy
<<: *svc_single_tenancy
QUARKUS_REST_CLIENT_ONECX_TENANT_URL: ${ONECX_REST_CLIENT_ONECX_TENANT_URL}
ONECX_TENANT_CACHE_ENABLED: ${ONECX_TENANT_CACHE_ENABLED}
TKIT_RS_CONTEXT_TENANT_ID_ENABLED: ${ONECX_RS_CONTEXT_TENANT_ID_ENABLED}
TKIT_RS_CONTEXT_TENANT_ID_MOCK_ENABLED: ${ONECX_RS_CONTEXT_TENANT_ID_MOCK_ENABLED}
...Environment variable set use for BFF services
onecx-announcement-bff:
...
environment:
<<: *bff_environment
...Environment variable set use for services with multi-tenancy awareness
onecx-announcement-svc:
...
environment:
<<: *svc_multi_tenancy
...Environment variable set use for services with single-tenancy awareness
onecx-iam-svc:
...
environment:
<<: *svc_single_tenancy
...Access Patterns
The following access patterns illustrate how different components of the OneCX Local Environment can be accessed.
- OneCX Shell
-
Main Entry Point
- Shell UI
-
http://onecx.localhost/onecx-shell/admin
All OneCX application UIs are accessed through the Shell workspace navigation - Workspace Management UI via Shell
- Workspace Microfrontend
- Workspace BFF
- Workspace Service
- Traefik Routing Rule
-
traefik.http.routers.onecx-workspace-ui.rule=Host(onecx.localhost) && PathPrefix(/mfe/workspace/)
See also the collection of utility services documented in Utilities.
Development Support
The Extend OneCX documentation describes how local running services are integrated into the OneCX Local Environment.