Adding Custom Certificates for Java Applications in Docker
The use of custom certificates solves issues with Java applications running inside Docker containers that need to communicate over HTTPS with services using non-standard or self-signed certificates.
Why is this about?
When running Java applications inside Docker containers, HTTPS connections often fail with errors like:
PKIX path building failed: unable to find valid certification path to requested targetAdd Custom Certificates
To resolve these issues, you need to add the required certificate to a Java Truststore used by your Java applications running inside Docker containers.
1. Get the Certificate
Identify and export the necessary certificate from the target HTTPS service.
Open the HTTPS website (where the error occurs) in your browser (here exemplarily Chrome).
- Click the icon left on URL, then
-
-
Click on Connection is secure
-
Click on Certificate is valid
-
Navigate to Details tab
-
Select the certificate with the target URL in Certificate Hierarchy
-
Click on Export and save as Base-64 encoded
.crtfile.
-
-
|
Alternatively, you can
|
Use the steps above to export all necessary certificates (root and intermediate CAs) that are required to establish a valid trust chain to the target HTTPS service.
certs/
├── YourCertificate.crt
└── YourCertificate2.crt2. Create a Java Truststore
Use the provided setup script to create or update a truststore with all your certificates.
The script automatically imports all .crt and .pem files from the specified directory.
In some cases, you will prompt to enter the root password for cleanup of existing entries.
./setup-truststore.shcerts/truststore.jks3. Verify the Truststore Contents
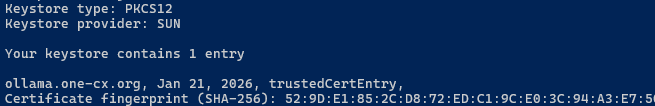
Optionally, you can check the contents of the truststore by listing all the certificates it contains using the following command:
keytool -list -keystore ./certs/truststore.jks -storepass trustjavaExpected output showing all imported certificates with their aliases.
4. Use Truststore in AI Service
Update your Docker Compose file to mount the truststore and configure Java to use it on the relevant services.
services:
onecx-ai-provider-svc:
image: ${ONECX_AI_PROVIDER_SVC}
volumes:
- ./certs/truststore.jks:/opt/certs/truststore.jks:ro
environment:
JAVA_TOOL_OPTIONS: >-
-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStore=/opt/certs/truststore.jks
-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword=trustjava
-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStoreType=JKSservices:
onecx-ai-provider-svc:
image: ${ONECX_AI_PROVIDER_SVC}
volumes:
- ./certs/truststore.jks:/opt/certs/truststore.jks:ro
entrypoint: ["/work/application"]
command:
- "-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStore=/opt/certs/truststore.jks"
- "-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword=trustjava"
- "-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStoreType=JKS"